Poker Chip Tool Pain Scale Age
- The Poker Chip Tool can be used to assess pain in children 4 to 12 years of age. The FACES pain rating scale can be used to assess pain for children 3 years of age and older. The VAS is indicated for use with older school-age children and adolescents. It can be used with younger school-age children, although less abstract tools are more.
- The AGS CoCare programs provide you with tools, resources, education, and support. AGS CoCare: Ortho TM is an evidence-based Geriatrics-Orthopedics Co-Management model that can be implemented throughout your health system. AGS CoCare: HELP TM provides the latest tools and hands-on guidance to make delirium prevention a reality.
- Poker Chip Tool Pain Scale Age Range
- Poker Chip Tool Pain Scale Age Calculator
- Poker Chip Tool Pain Scale Age List
- Poker Chip Tool Pain Scale Age Guide
Tools for measuring pain: 290000: Tools for measuring pain: Tools for measuring pain: T: English: Pain/Anaesthesia: Child (0-12 years);Teen (13-18 years). This software is provided by Classic Poker Chips for designing chips using our currently available options. For more information and to place orders, please visit our website or email us. The graphics in this software were provided by J5 (John Faulhaber). John is available for freelance custom inlay design work and has produced many of the. Fall Assessment Tool The Humpty Dumpty Scale Parameter Criteria Score Age Less than 3 years old 4 3 to less than 7 years old 3 7 to less than 13 years old 2 13 years old and above 1 Gender Male 2 Female 1 Diagnosis Neurological Diagnosis 4 Alterations in Oxygenation (Respiratory Diagnosis, Dehydration, Anemia.

This material must not be used for commercial purposes, or in any hospital or medical facility. Failure to comply may result in legal action.
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Nov 16, 2020.
- Care Notes
- Overview
What do I need to know about my child's pain?
Poker Chip Tool Pain Scale Age Range
Children feel and express pain in different ways. Your child may or may not be able to tell you he is in pain. Something that may be painful to one child may not be painful to other children. Your child's pain may be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term). Pain management is an important part of your child's care.
How will I know if my child is in pain?

If your child can talk, he may tell you where he hurts and how bad it is. If you have a baby or small child, you may need to watch them for signs of pain. You may notice the following behaviors:
- Restlessness
- High-pitched crying
- Not moving or holding himself in a position to decrease pain
- Pulls away or gets upset when he is touched
- Touches, tugs, or rubs the part of his body that is painful
- Eats less or not at all
- Sleeps more or less than usual
What is a pain scale?
A pain scale is a tool used by your child's caregiver to help measure your child's pain. Your child's caregiver uses the pain scale together with examining your child. Your child's caregiver may use any of the following pain scales:
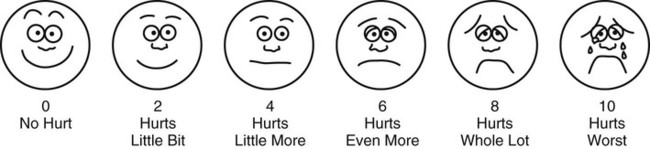
- Faces pain scale: This scale consists of different faces, from happy (no pain) to sad (a lot of pain). Your child may be asked to point to the face that best shows how he feels.
- Body outline tool: Your child will be asked to mark an X or color the painful area on a drawing of a child's body. Different colors can be used to measure his pain.
- Colored analog scale: This scale assigns colors to mild, moderate, or severe pain. Your child will be asked to point to the color that shows how much pain he is in.
- Oucher scale: This scale is used in children who can count. Your child will be asked to point to a number from 10 to 100 to show the amount of pain he is in.
- Poker chip tool: Your child will be asked to pick the number of poker chips to show the level of his pain. One chip represents a small amount of pain and 4 chips is the most amount of pain.
What medicines are used to control pain?
- Ibuprofen or acetaminophen: These medicines help decrease your child's pain. They can be bought without a doctor's order. Ask how much medicine is safe to give your child and how often to give it.
- Narcotic analgesics: These medicines include codeine and morphine. They are used for moderate to severe pain.
- Patient-controlled analgesia (PCA): This is a device that uses an electric pump to give your child pain medicine through an IV. The IV is placed in your child's vein, usually in his arm. Your child receives medicine by pushing a button. Ask your child's caregiver for more information about PCA.
- Anesthetics: These may be injected in or around a nerve to make your child more comfortable. It works by blocking pain signals from the nerves.
What are the side effects of pain medicines?
- Nausea, vomiting, or constipation
- Itching
- Pain in the lower abdomen or trouble urinating
- Irregular heartbeat or seizures
- Trouble breathing
Why is pain control important?
If pain is not treated, it can decrease your child's appetite and affect how well he sleeps. It may also decrease his energy and ability to do things. Pain may also change your child's mood and relationships with others. If pain is treated, your child will feel better and may heal more quickly.
How can I help manage my child's pain?
- Give your child his pain medicine as directed: Follow instruction on how much and how often to give your child medicine.
- Do not wait until your child's pain is severe: The medicine may not work as well at controlling the pain if you wait too long to give it. Tell your child's caregiver if your child's pain gets worse.

When should I contact my child's caregiver?
Poker Chip Tool Pain Scale Age Calculator
Contact your child's caregiver if:
- Your child has a fever.
- Your child has nausea or vomiting.
- Your child is more sleepy than usual after he takes his medicine.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
When should I seek immediate care?
Seek care immediately or call 911 if:
- Your child's skin becomes red, swollen, and itchy.
- Your child suddenly has trouble breathing.
- Your child is sad, depressed, or not able to cope with his pain or illness.
- Your child's pain does not get better, or he has new pain.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your child's care. Learn about your child's health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your child's caregivers to decide what care you want for your child.
Poker Chip Tool Pain Scale Age List
Further information
Poker Chip Tool Pain Scale Age Guide
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.